Phishing
Phishing attacks are the practice of sending fraudulent communications that appear to come from a reputable source.
Phishing attacks try to create a sense of urgency or fear (known as "social engineering"). Slow down and evaluate:
- sender:
- public email domain (e.g., gmail) - not authentic
- unkown contact
- known or trusted (e.g., business or company) but could be compromised - known as targeted spear phishing
- suspicious links:
- context appears correct across multiple subdomains, however domain name and top level domain are suspicious
- long uuid or key in querystring to hide domain name
- suspicious payload (malicious attachments)
- poorly written wording, punctuation mistakes etc.
- common sense, e.g., you will never be asked for your credentials via email or text
- use zero trust security:
- never accept anything at face value and assume everything is hostile
- always continuously verify every person or device seeking access to a network or data
Evaluate this free $100 iTunes gift card website for a potential phishing attack:
Free $100 iTunes gift card website
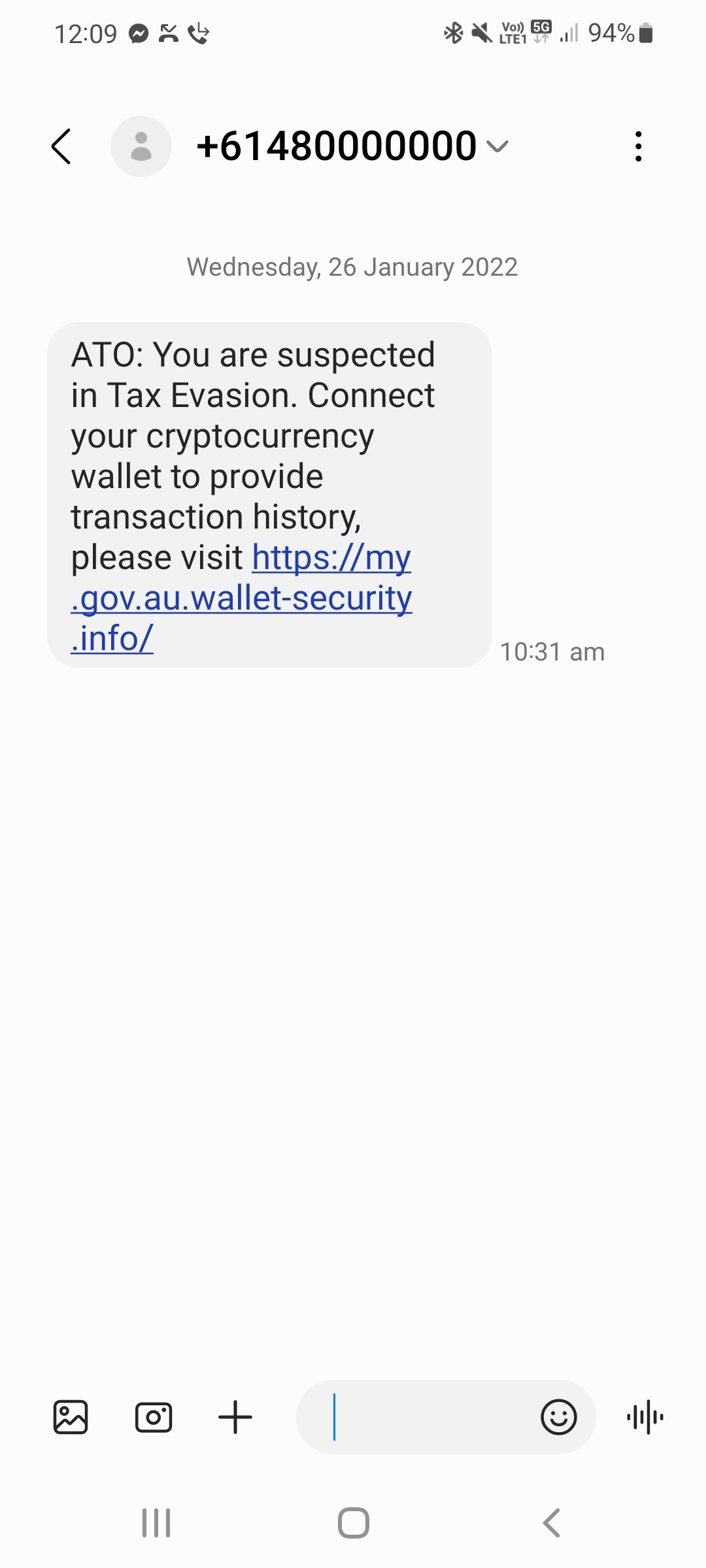
Evaluate this text message for a potential phishing attack: